How does the body absorb orally taken liposomal vitamins?
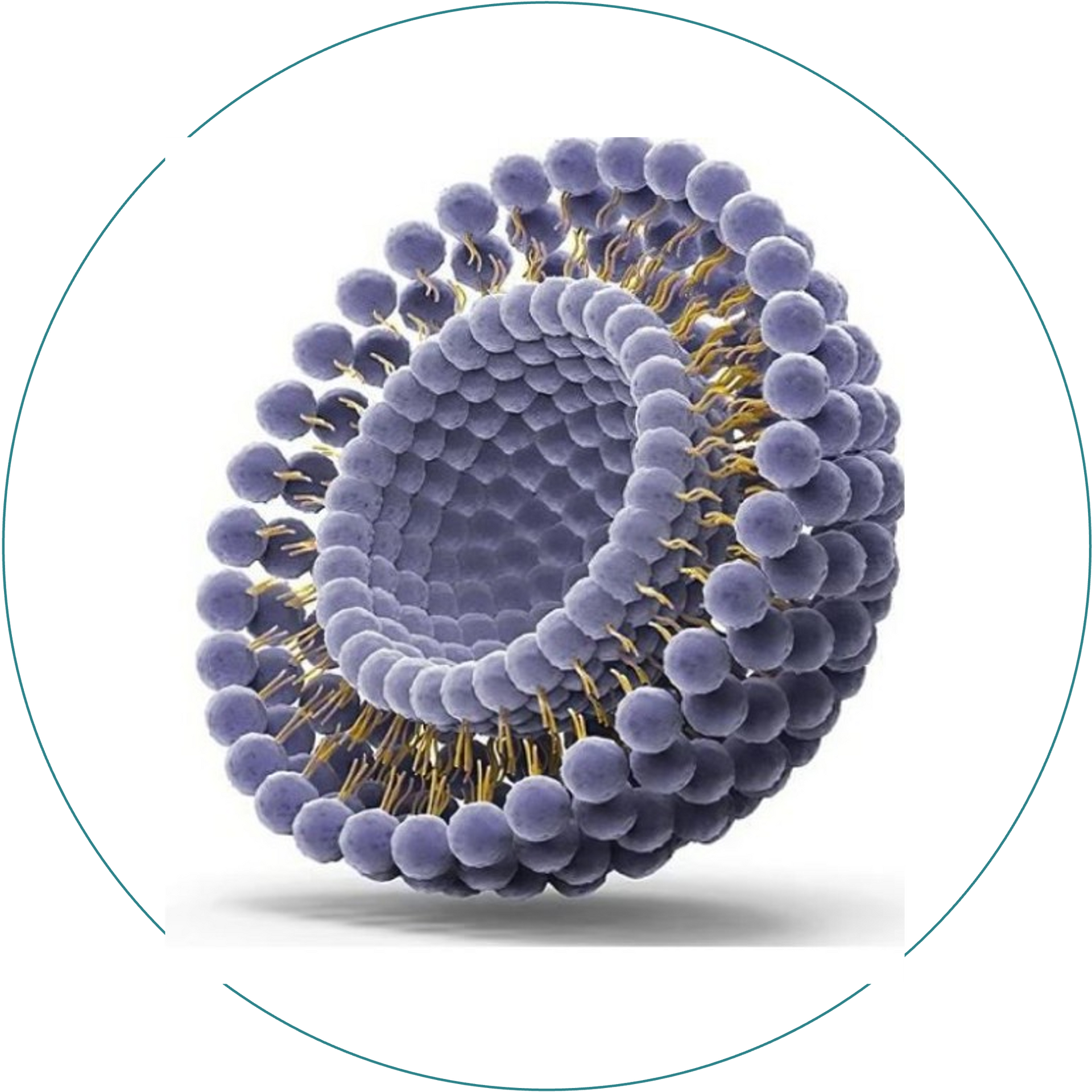

Liposomal Technologies
Liposomes are small phospholipid vesicles designed for superior absorption and activity for active ingredients.
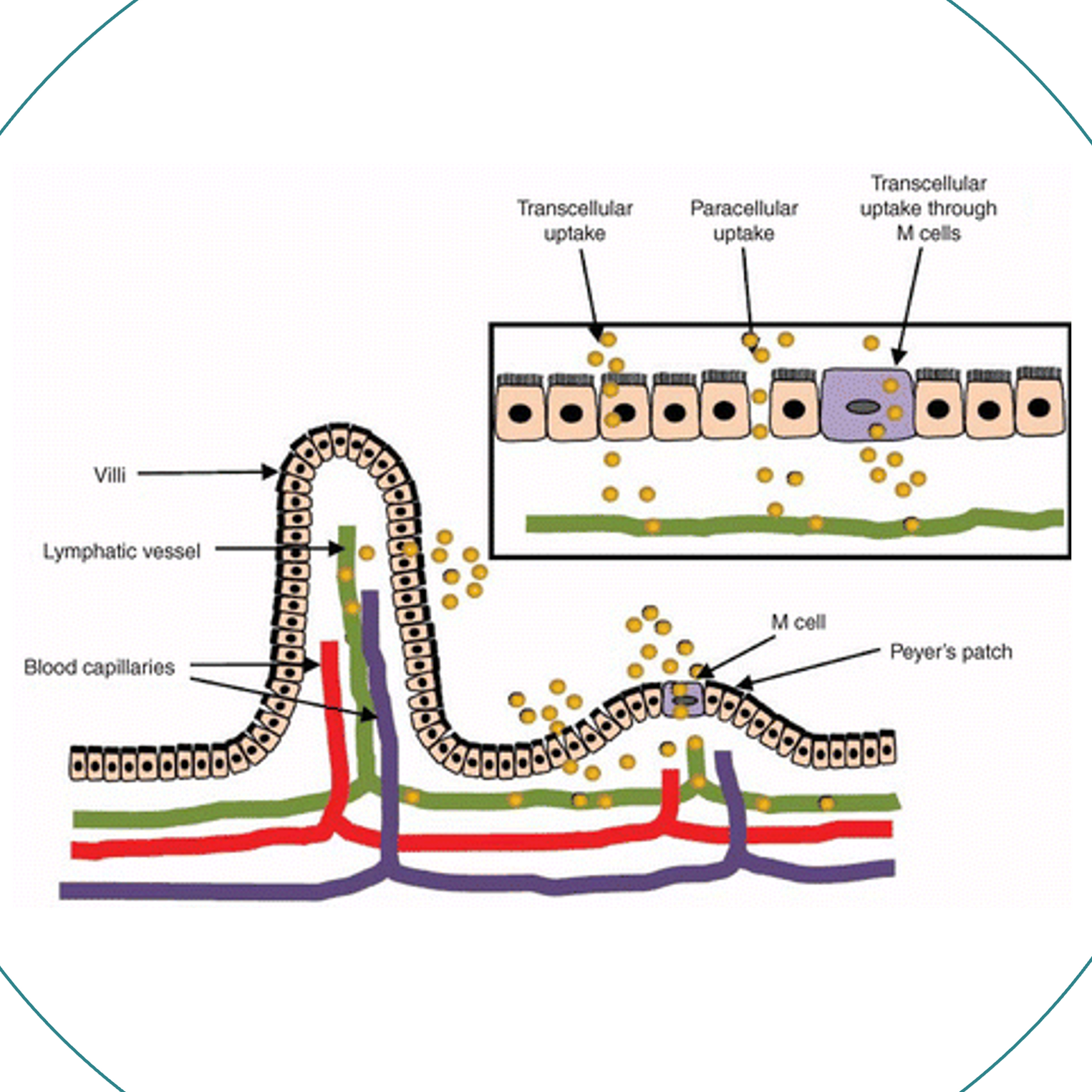
Absorption in Body
Liposomes enter via M Cells to reach the lymph duct. The lymph delivers the liposomes into the blood in high portions.
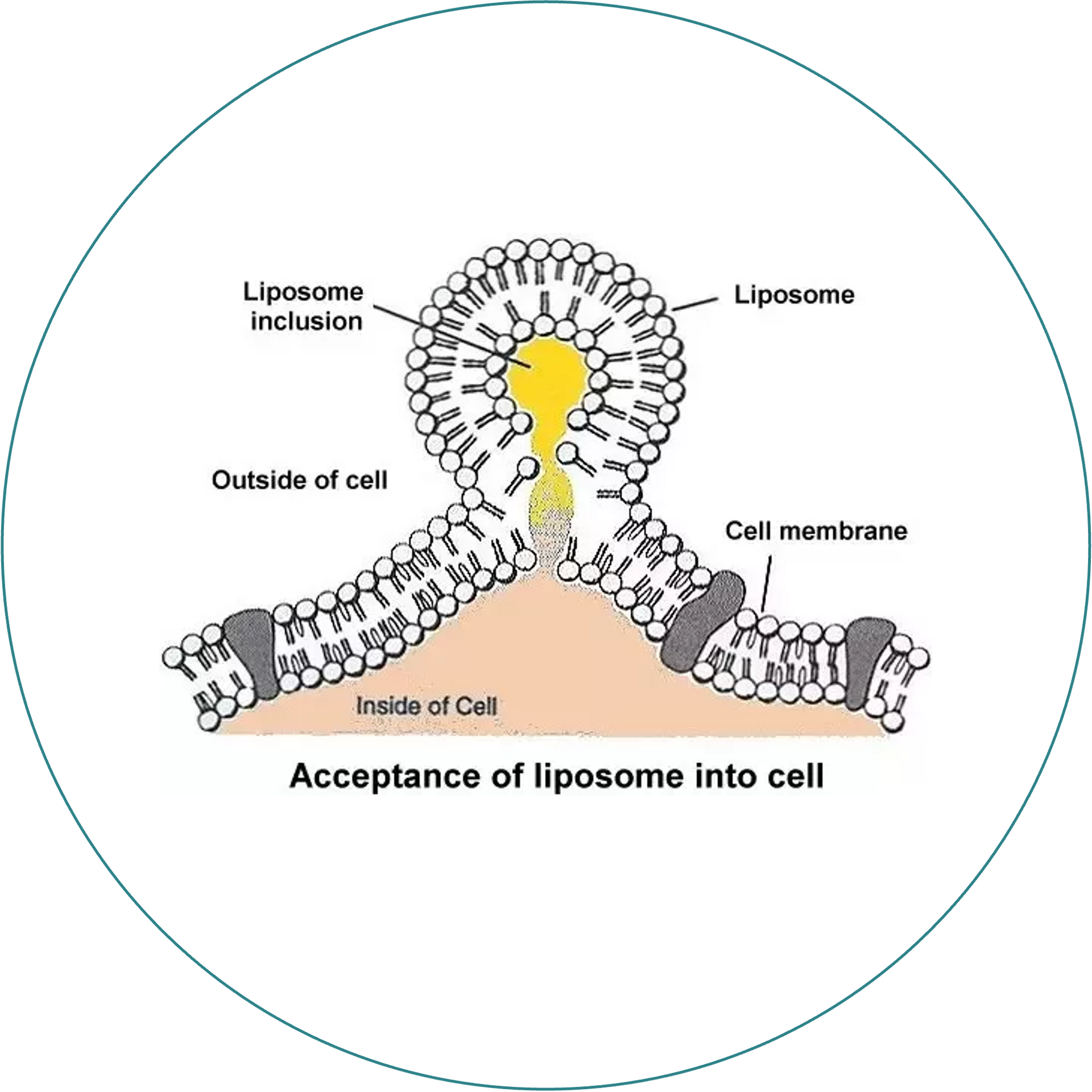
Cell Uptake
The phospholipid encapsulation of the liposome can fuse with the phospholipid membrane of the cells, delivering the active ingredient into the cell.
How are liposomes produced?
Liposomal encapsulation is a phenomenon that occurs in liquid milieu, the hydrodynamic forces are required to perform the encapsulation of the active ingredients with phospholipids.
The electrostatic potential (zeta potential) and the pressure of the liquid milieu helps to maintain the stability of the liposome. Therefore, liposomes were thought to exist only in liquid form.
Recent developments in the liposomal encapsulation technologies succeeded to develop dry powder liposomes. lipoNIQ® uses a technology achieve the required Zeta Potential values. Powder liposomes are extremely stable if done well.
Proven Absorption with lipoNIQ® liposomes by Caco-2 Cell Line tests
lipoNIQ® uses a cutting-edge technology of double encapsulation of the active ingredients with phospholipids and natural polymers to achieve required Zeta potential values and thus protect the liposomal ingredients from the harsh digestive environment of the stomach, reaching the bloodstream intact.
lipoNIQ® liposomes are quality tested for its particle size, zeta potential and gastric stability
Particle Size Analysis: Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) result of lipoNIQ® product - value between 150 - 400 nm defines superior quality and bioavailability.
Zeta Potential result of lipoNIQ® product. Value between 20 to 40 mV is important to block degradation of ingredient in GIS and thus provides superior bioavailability.
Gastric Stability explained: Testing the liposome in different ph environments is necessary to proof the integrity of the liposome in the Gastro Intestinal System.
